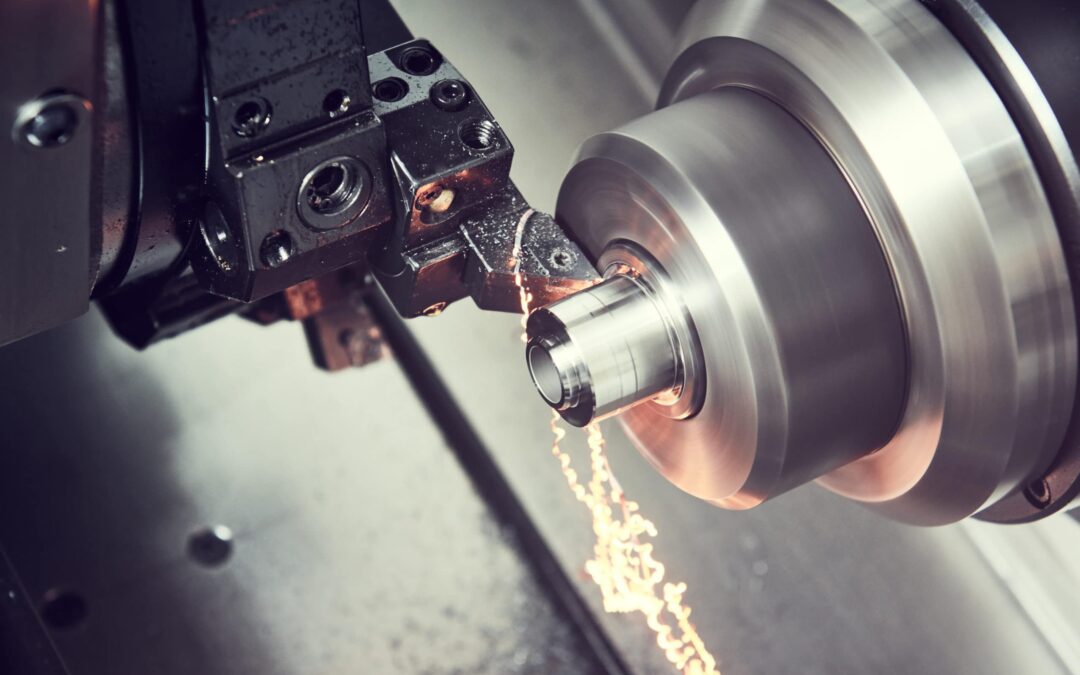
Lathes are essential tools in the world of machinery and manufacturing. Whether you are an aspiring entrepreneur, a seasoned business leader, or simply curious about how these machines operate, understanding the intricacies of lathes can be incredibly beneficial. In this article, we will explore how lathes work, their components, and their significance in various industries.
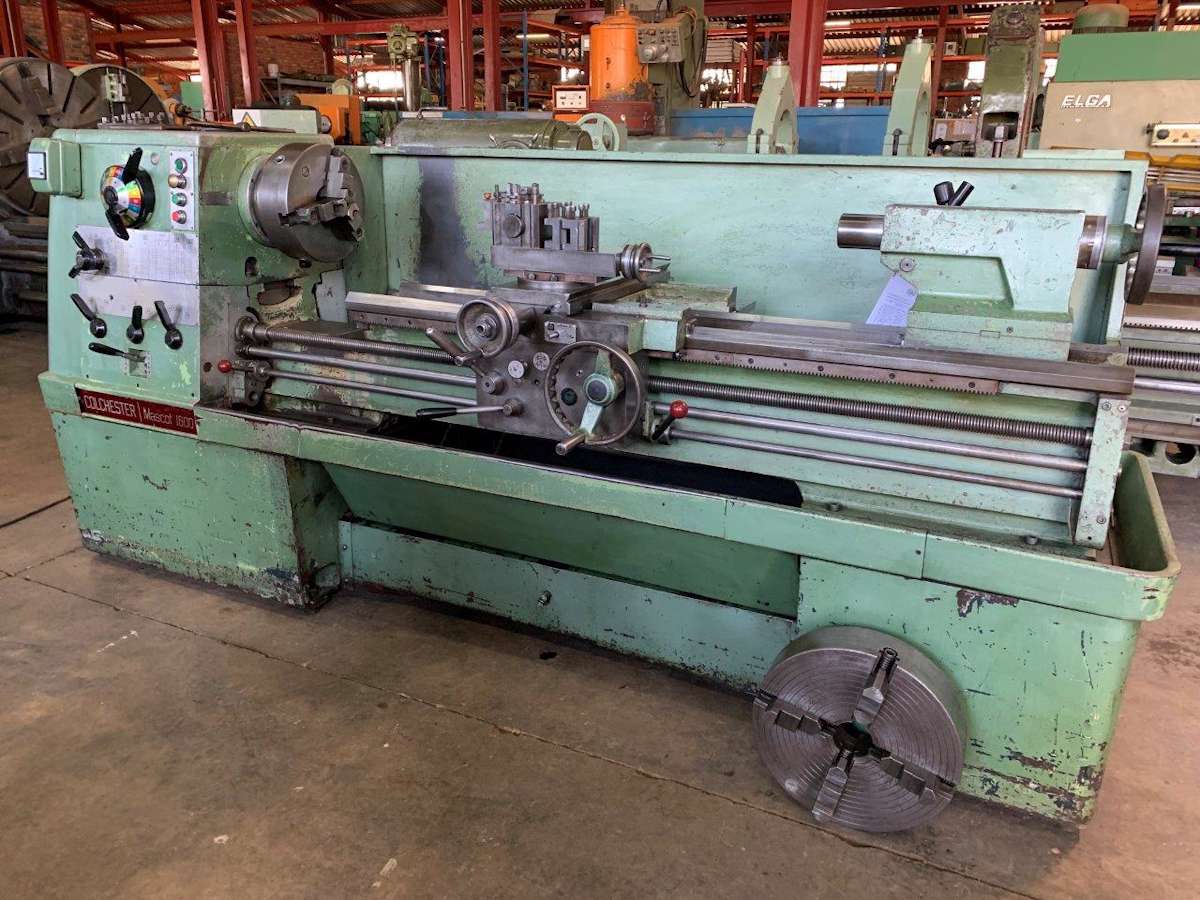

What is a Lathe?
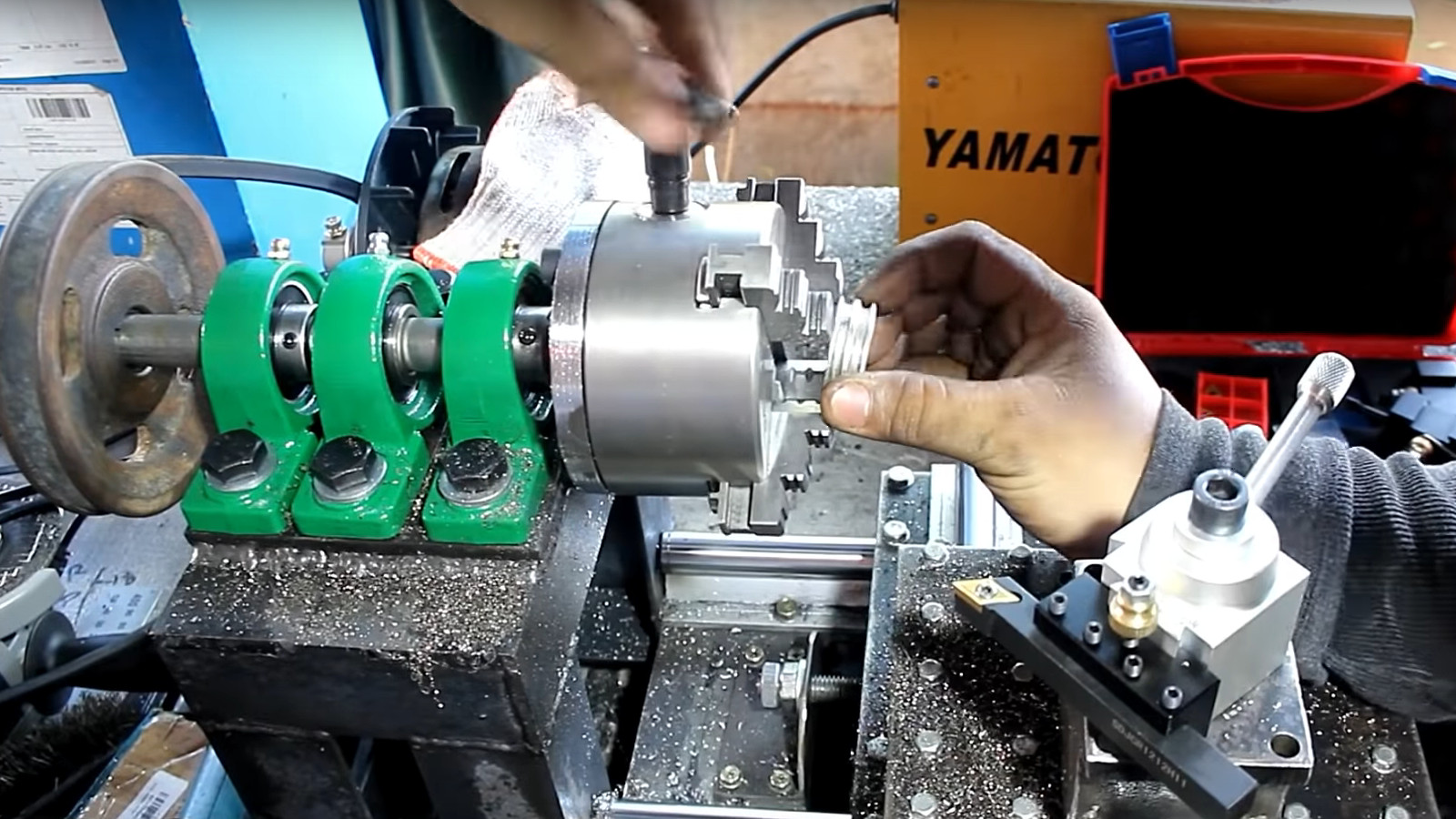
A lathe is a machine tool used primarily for shaping materials such as metal, wood, and plastic. The process involves rotating the workpiece on its axis while a cutting tool is applied to the material to shape it into the desired form.
Components of a Lathe
Bed
The bed is the base of the lathe. It provides support for the whole structure and ensures stability during operations.
Headstock
The headstock houses components that rotate the workpiece, such as the main spindle and drive mechanism.
Tailstock
This component supports the end of a long workpiece by providing alignment and additional support as needed.
Carriage
The carriage holds the cutting tool and moves along the bed to facilitate the shaping of the material. It is crucial in determining the accuracy of the workpiece.
How Lathes Work
The basic operation of a lathe involves securing a workpiece in the headstock and rotating it. The cutting tool, mounted on the carriage, moves along the workpiece to remove material and create the desired shape. Lathes offer precision and consistency, making them indispensable in countless applications.
Types of Lathes
Engine Lathes
Widely used in general machining, these lathes are versatile and can handle a variety of materials and sizes.
Turret Lathes
Ideal for production work, turret lathes simplify repeat operations by allowing multiple tools to be used simultaneously without changing settings.
CNC Lathes
The advent of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology has revolutionized traditional lathes. CNC lathes integrate computer-aided design and automation, allowing for enhanced precision and efficiency.
Significance of Lathes in Industry
Lathes play a critical role in the manufacturing and engineering sectors. They are used to produce components for automobiles, electronics, and aerospace applications, among others. As industries strive for precision and productivity, lathes continue to be pivotal in meeting these demands.
Innovations in Lathe Technology
With advancements in technology, modern lathes are integrated with features that improve functionality and precision. For instance, the introduction of innovative ML algorithms in leak detection systems has parallels in the development of CNC lathes. You can read more about such innovations on sensors innovation.
The Role of Lathes in the Future
As industries evolve, the demand for high-quality custom components grows. Lathes, with their capacity for precision, customization, and adaptability, will remain crucial assets in the future of manufacturing.
Conclusion
Understanding how lathes work and their industrial significance can provide valuable insights into their versatile applications. Entrepreneurs and business leaders stand to benefit from this knowledge, enhancing operational efficiency and exploring new opportunities in various sectors. For further in-depth reading on how lathes work, check this external resource: Lathe Functionality.
FAQs
1. What materials can lathes work with?
Lathes can work with a variety of materials including metal, wood, plastic, and more. The choice of material depends on the application and the specifications of the finished product.
2. What safety precautions should be taken when using a lathe?
When operating a lathe, wearing appropriate personal protective equipment, ensuring a clean work area, and following the machine’s operational guidelines can help prevent accidents.
3. How do CNC lathes differ from traditional lathes?
CNC lathes use computerized systems to control the movement and operation of the machine, offering greater precision and efficiency compared to traditional lathes, which rely on manual operation.
This article contains affiliate links. We may earn a commission at no extra cost to you.

